Table of contents
1- Part #3 recap
2- Regression Model & Results
3- Discussion
4- Limitations & Implications
Part #3 recap
In part #3, we conducted descriptive analysis to examine the distribution of sample characteristics for our study. We provided a summary of the demographic characteristics, mental health outcomes, and binge drinking variables. In this post, we will continue our analysis and complete a logistic regression analysis to identify any significant predictors of negative mental health among veterans with disabilities in our sample.
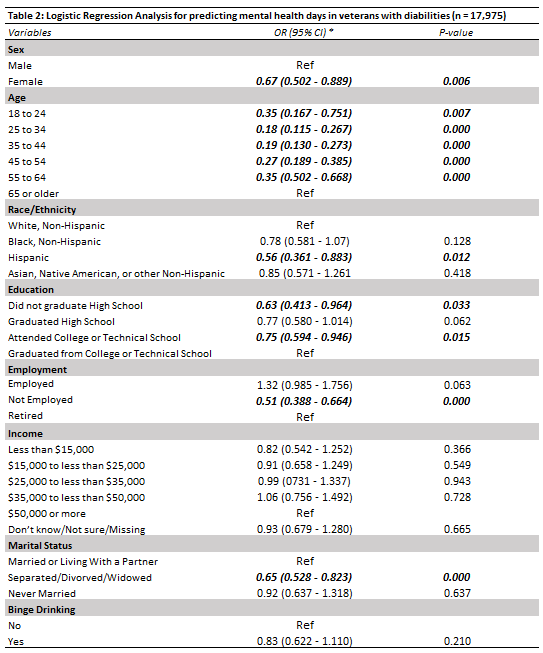
Regression Model & Results
After conducting our logistic regression on STATA, we organized the results in the Table 2 below. Here are some insights we found:
- Variables (sex, age, marital status) were significant predictors of having 14 or more mentally unhealthy days. For example, compared to people who were married or live with a partner, people who were seperated, divorced, or widowed were 0.65 times more likely to have 14 or more bad mental health days.
- Similarly, individuals who were not employed were 0.51 times more likely to report 14 or more negative mental health days compared to retired people.
- In contrast, binge drinking was not a significant predictor of bad mental health days in this specific sample.
Discussion
Although not all the results of this study were consistent with the findings of the literature review, some of the significant findings were in line with the reviewed studies. For example, the CDC highlights lack of employment as one of the major stressors for people with disabilities (CDC, 2020). In addition, our literature review emphasizes that difficulties during transition (for example, difficulties finding and maintaining employment) are major contributors of stress veterans (NIDA, 2019). Some other variances in the results of this study, when compared to the literature review, can be attributed to the limitations mentioned in the section below.
Limitations & Implications
This study has limitations. First, this study is cross-sectional and we cannot infer causal relationships. Second, the population we selected is very specific and if we were to take more years it might give us more informative outcomes. Third, we identified (veterans with disabilites) by identifying disability variables and veteran variable. There is a difference between veterans with disabilities and disabled veterans. Therefore, if the study was conducted on disabled veterans, the analysis might have given us different results.
Measuring HRQOL can help in determining the impact of alcohol use among veterans with disabilities. Additional evidence is needed to understand how alcohol use can impact mental health outcomes for veterans with disabilities. This study builds on existing knowledge by using new data from the 2020 BRFSS to yeild a national sample.